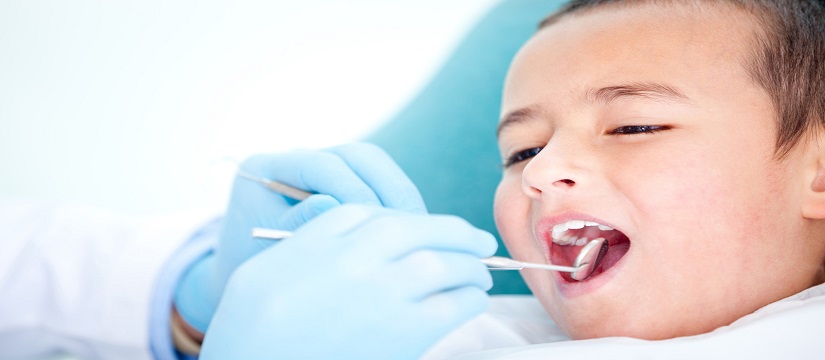
Child Dentistry / Pedodontics
Pedodontics, or pediatric dentistry, is a specialized branch of dentistry for the treatment of children.
Pedodontics or paediatric dentistry as it is known at a lot of places is one of the most challenging aspects of dentistry as it sometimes involves taking care of patients who are below the age of reason and don’t necessarily always know what is best for them. Therefore we at smilekonnekt take our children seriously and provide dental care by a team of pedodontists.
Pedodontics or Pediatric Dentistry refers to a branch of dentistry that specializes in dental care for children under the age of 16. Pediatric dentists require an extra two to three years of dental training that prepare them in meeting the unique dental needs of infant, children, and adolescent dental care. This also includes those with special health care needs.
Differentiating itself from regular dentistry, pediatric dentistry emphasizes the establishment of trust and confidence in children with their dentists. Consequently, one of the main components of pediatric training is child psychology. This manifests itself in special office designs, different communication style, and an emphasis on teaching preventative dental habits to children in an effort to make dental visits enjoyable.
For children, pedodontics place special importance in preventing tooth decay. Studies show that poor oral health care in children lead to decrease school performance and poor social relationships. Therefore, pediatric dentists give advice on how to make teeth strong, the importance of developing healthy eating habits, and other ways to prevent cavities from occurring.
Additionally, pediatric dentists work towards the maintenance of primary teeth (baby teeth) until they are naturally lost. This is due to the importance they serve in permitting children to chew properly and therefore maintain good nutrition, its role in speech development, and the way it aids permanent teeth by saving space for them.
The role of the pediatric dentists changes as children enter adolescence. Recognizing the growing importance of appearance and self-image in their clients, pediatric dentists work to ensure that adolescents’ dental needs are met. Preventative dental health care is emphasized and when necessary, information is provided to adolescents about subjects such as wisdom teeth, tobacco use, sealants, and oral piercing.
Pedodontics not only aids in the dental health of children but serves as an educational tool for parents. It is recommended that a dental visit should occur between shortly after the presence of the first tooth in a child to that child’s first birthday. This is because early mouth examinations aids in the detection of the early stages of tooth decay and can therefore be immediately treated. Additionally, parents are given a program of preventative home care (brushing, flossing, fluorides), a caries risk assessment, the latest facts on finger, thumb and pacifier habits, advice on preventing injuries to the mouth and teeth of their children, and information on growth and development.
Procedures
- All restorations
- Space maintainers
- Crowns
- Root canal treatment
- Special service under sedation
FAQs
“The sooner, the better!” The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry States that parents should begin dental cleaning at birth, by cleaning their child’s gums with a soft infant toothbrush and water. Unless it is advised by your child’s pediatric dentist, fluoridated toothpaste is not recommended until 2-3 years of age.
“First visit by first birthday” According to the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, children should first visit the dentist when they receive their first tooth or by the child’s first birthday. Early dental care is important for dental prevention in the future. However, dental problems can begin early. A major dental concern for young children is Early Childhood Caries, also known as baby bottle tooth decay or nursing caries.
To prevent tooth decay in young children, the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry; recommends that children be encouraged to begin drinking from a cup as they approach their first birthday. At nap times or at night, children should not fall asleep with a bottle. It is recommended that nighttime breast-feeding be avoided after the first primary (baby) teeth begin to erupt. Drinking juice or other sugary drinks from a bottle should always be avoided. When such drinks are offered, they should be served in a cup.